打开文本图片集
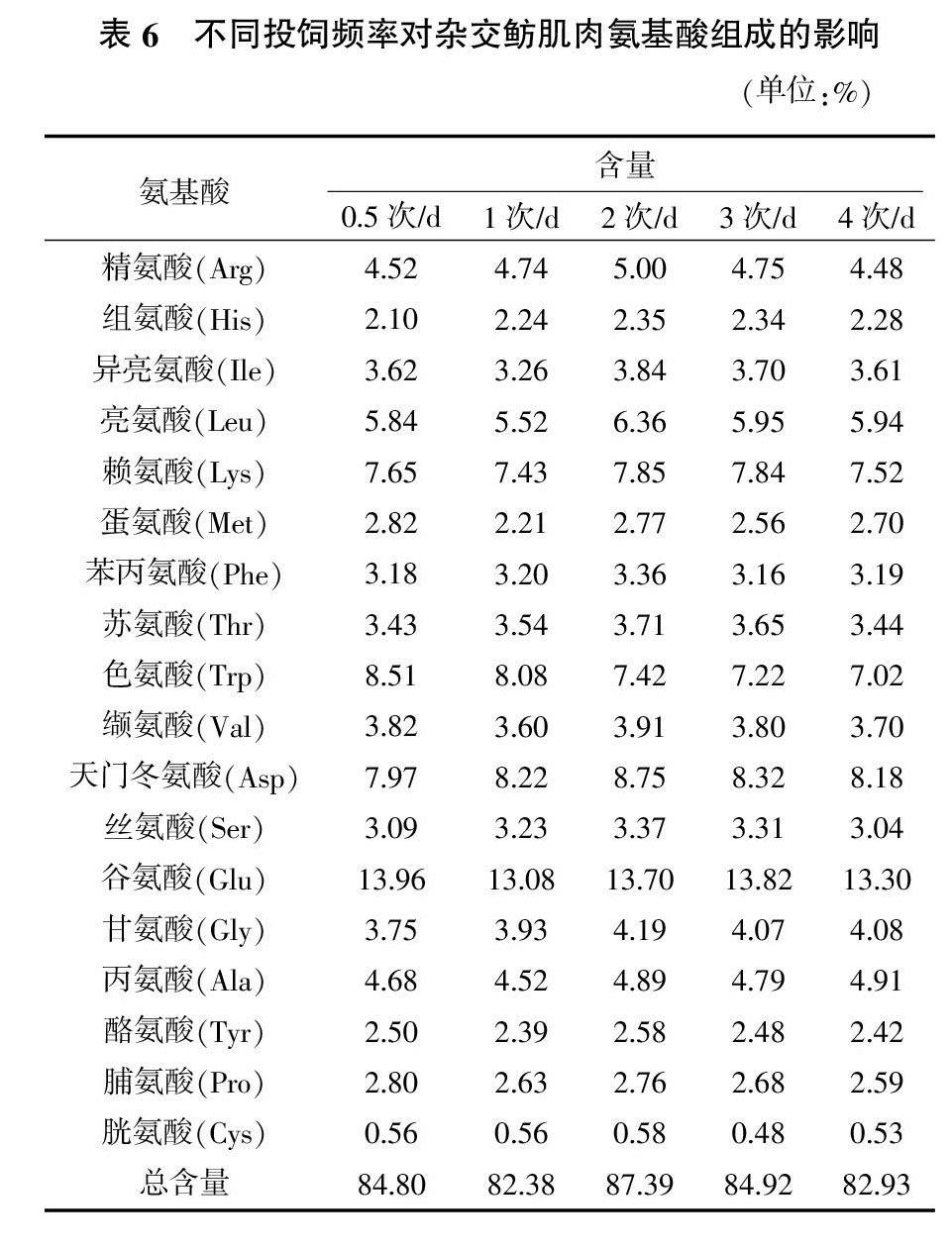
摘要:为研究投饲频率对杂交鲂生长、饲料利用、消化酶活性及鱼体生化组成的影响,在室外微流水水槽中以配合饲料按0.5、1、2、3和4次/d的投饲频率分别投喂杂交鲂幼鱼8周。结果表明,投饲频率从0.5次/d增加至3次/d时,杂交鲂的体增重显著增加,随后投饲频率从3次/d增加至4次/d时,体增重并未显著提高。杂交鲂的摄食率和鱼体脂肪含量随着投饲频率的增加而显著增加,而试验鱼的肠道胰蛋白酶活性和鱼体水分含量则显著降低。饵料系数随着投饲频率的增加呈现先降低后增加的趋势,且0.5次/d组最高,而2次/d和3次/d组最低。各试验组之间的肠道淀粉酶活性、肠道脂肪酶活性、鱼体的蛋白质含量、灰分含量及肌肉氨基酸组成均无显著差异。杂交鲂的适宜投饲频率为3次/d,其饲料利用效率最高。
关键词:杂交鲂;投饲频率;体增重;饲料利用;消化酶;鱼体生化组成
中图分类号:S964.3 文献标识码:A
文章编号:0439-8114(2019)08-0105-05
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.08.024 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Abstract: An eight-week feeding trial was conducted to examine the growth, feed utilization, digestive enzymes and body composition of juvenile hybrid bream at different feeding frequencies. Fish were fed a test diet at 0.5,1,2,3 or 4 meals/d. The weight gain significantly increased with increase in feeding frequency from 0.5 to 3 meal/d, and afterward did not change with feeding frequency from 3 to 4 meal/d. With the increasing of feeding frequency, the feed intake and body lipid content of fish significant increased, while intestinal trypsin activity and body moisture content of fish significant decreased. The feed conversion ratio exhibited a downward trend first and then an upward trend, with the increasing of feeding frequency, and fish fed 0.5 meals/d exhibited highest FCR, while fish fed 2 and 3 meals/d exhibited lowest FCR. No significant differences were found in intestinal amylase activity, intestinal lipase activity, body crude protein content, body ash content and muscle amino acid composition among all the feeding frequencies. The present study reveals that the optimum feeding frequency is 3 meals/d for hybrid bream with the highest feed utilization.
Key words: hybrid bream; feeding frequency; weight gain; feed utilization; digestive enzyme; body composition
当饵料营养完全满足鱼类的生长需求时,投饲策略是提高鱼类养殖效益的有效措施[1]。合理的投饲策略不仅可以减少饵料的浪费,同时也可降低养殖鱼类对水体环境的负面影响[2],而不恰当的投饲策略将导致鱼类养殖成本增加、个体差异变大、成活率降低等[3]。鱼类的投饲策略主要包括投饲时间、投饲频率、投饲水平及摄食节律等方面。目前,相关学者已广泛评估多种养殖鱼类的投饲水平和投饲频率等饲喂制度[4-6]。研究发现,适宜的投饲频率不仅能提高养殖鱼类的生长性能和饲料利用效率,也能降低养殖管理过程中的劳动力成本與饲养成本[7,8]。可见,投饲频率是一种相对实用的投饲策略[9]。
杂交鲂是以三角鲂(Megalobrama terminalis Richardson,♀)为母本、翘嘴红鲌(Erythroculter ilishaeformis,♂)为父本杂交而得到的新品种。杂交鲂是一种杂食性淡水养殖鱼类,体型较大。由于杂交鲂的生长速度快、适应环境能力强、营养组成丰富等特点,已成为浙江、江苏等省广泛养殖的新品种[10]。目前,有关杂交鲂的饲喂制度均基于1 d投喂两次,对杂交鲂适宜的投喂时间和投饲频率缺乏系统研究。为此,本研究旨在查明优化杂交鲂生长、饲料利用效率、消化酶活性和鱼体生化组成的最佳投饲频率,以期为杂交鲂商业化池塘养殖提供合理的管理策略。
1 材料与方法
扩展阅读文章
推荐阅读文章
花田文秘网 https://www.huatianclub.com
Copyright © 2002-2018 . 花田文秘网 版权所有